Introduction
When dealing with skin conditions like ringworm and eczema, choosing the right treatment can be a bit of a puzzle. Both conditions have a range of treatments available, from over-the-counter (OTC) options to more potent prescription remedies. In this guide, we’ll dive into the differences between these treatments, helping you make an informed choice for your skin health.
Understanding Ringworm
What is Ringworm?
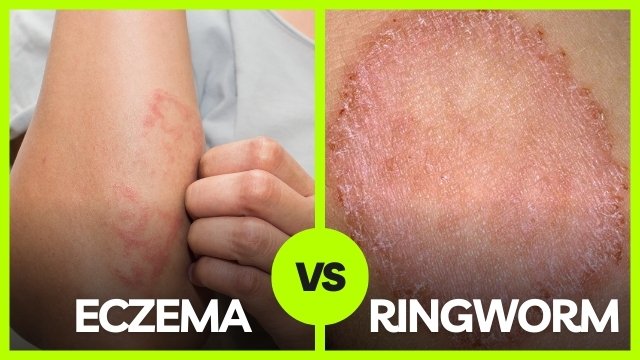
Ringworm isn’t a worm; it’s a fungal infection that creates a ring-shaped rash. This infection, also known as tinea, is caused by fungi that thrive on the skin’s surface. It’s highly contagious and can spread through contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of Ringworm
Common symptoms of ringworm include itchy, red, and scaly patches on the skin. These patches often have a ring-like appearance with a clearer center. The rash can appear anywhere on the body but is most common on the arms, legs, and scalp.
Understanding Eczema
What is Eczema?
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition that causes inflammation, redness, and skin irritation. Unlike ringworm, eczema is not caused by a fungal infection but by genetic and environmental factors. It often flares up in response to allergens, irritants, or stress.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms include dry, itchy skin that can become red and inflamed. In severe cases, the skin may crack, bleed, or ooze. It commonly affects areas like the elbows, knees, and face.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Ringworm Treatments
Topical Antifungals
For ringworm, OTC topical antifungals are often the first line of defense. These include creams, lotions, and powders that can be applied directly to the affected area. Popular choices are clotrimazole and miconazole, which work by killing the fungi causing the infection.
Antifungal Creams and Powders
OTC antifungal creams like Lotrimin and Tinactin are effective for treating mild cases of ringworm. They typically require application twice daily for a few weeks. Powders can also help keep the affected area dry, which helps prevent the fungi from thriving.
Eczema Treatments
Moisturizers and Emollients
OTC moisturizers and emollients are essential for eczema. Products like Aquaphor and Cetaphil help lock in moisture and create a barrier to prevent the skin from drying out. Regular application can reduce itching and inflammation.
Topical Steroids
OTC topical steroids, such as hydrocortisone cream, can help reduce inflammation and itching. They are usually recommended for short-term use to manage flare-ups and should not be overused to avoid potential side effects.
Prescription Treatments
Ringworm Treatments
Oral Antifungals
For more severe or resistant cases of ringworm, prescription oral antifungals might be necessary. These medications, such as terbinafine or itraconazole, work from within the body to eliminate the infection. They are typically prescribed when topical treatments fail, or the infection covers a large area.
Prescription Topical Antifungals
Stronger prescription topical antifungals, like ketoconazole, are available for cases that do not respond to OTC options. These are often used for more stubborn or extensive infections and may require a longer treatment.
Eczema Treatments
Stronger Topical Steroids
When OTC treatments are not sufficient, stronger prescription topical steroids might be required. These include medications like betamethasone or fluocinonide, which provide more potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
For those who cannot use topical steroids or prefer an alternative, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus are an option. These medications help to modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation without the side effects of steroids.
Comparing Effectiveness
Ringworm: OTC vs. Prescription
OTC treatments are often effective for mild to moderate ringworm infections. They are convenient and usually sufficient for most cases. However, prescription treatments might be necessary to eradicate the fungi if the infection is severe or persistent.
Eczema: OTC vs. Prescription
OTC treatments for eczema, especially consistent use of moisturizing cream, can effectively manage symptoms in many cases. However, for more severe eczema or when OTC treatments fail, prescription options can provide more significant relief and control over symptoms.
Side Effects and Considerations
Ringworm Treatments
OTC antifungals are generally well-tolerated but can cause mild irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. Prescription oral antifungals may have more serious side effects, such as liver damage or gastrointestinal issues, so they should be used under medical supervision.
Eczema Treatments
OTC moisturizers and steroids are generally safe but should be used as directed to avoid potential side effects like skin thinning. Prescription steroids and calcineurin inhibitors may have more pronounced side effects, so it’s important to follow your doctor’s guidance.
When to Seek Professional Help
If OTC treatments don’t provide relief or symptoms worsen, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent or severe cases of ringworm and eczema may require prescription medications and a tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
Choosing between over-the-counter and prescription treatments for ringworm and eczema depends on the severity of your condition and how well OTC options work. Both approaches have their merits, and understanding their differences can help you make the best decision for your skin health. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment.
To read more articles click here.